How to Create A Simple API: ExpressJS
Creating an Express API in less than 5 long minutes (technical tutorial)
Express JS is a backend framework that runs on Node JS.
It really comes in handy when creating backend microservices for our applications.
I will take you through simple steps in creating a simple API with Express.
Installing dependencies
This should be the simplest of all:
On the project root, open up your terminal/CMD and install express using the following command:
npm install express
Create a server file
While still on the root of your project, create a JavaScript file; app.js
Creating A server:
On the newly created file (app.js), let's create a simple server:
// importing express
const express = require('express')
// creating a instance of express
const app = express();
After bringing express into the app, let's create a simple server:
app.listen(5000, console.log('App Running On Port 5000!'))
The .listen() method binds and listens for connections on the specified host and port.
Your file should now have the following code:
// importing express
const express = require('express')
// creating a instance of express
const app = express();
app.listen(5000, console.log('App Running On Port 5000!'))
On your terminal, run the server using:
node app.js
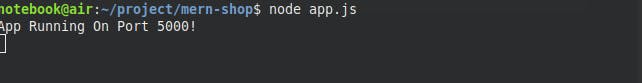
When you see the message: 'App Running On Port 5000!' on your terminal, well! you are good to GO.
Getting the API
Well normally, your backend application will be sending data to a client site, let's create a simple server.
On the same folder, create a new file "data.js" with the following data:
const colors = [
{
color: 'red',
value: '#f00',
},
{
color: 'green',
value: '#0f0',
},
{
color: 'blue',
value: '#00f',
},
{
color: 'cyan',
value: '#0ff',
},
{
color: 'magenta',
value: '#f0f',
},
{
color: 'yellow',
value: '#ff0',
},
{
color: 'black',
value: '#000',
},
]
module.exports = colors
let's write the code to server the data from the file from our server:
// getting the data file
const color = require('./data')
// serving data
app.get('/api/colors', (req, res) => {
res.send(color)
})
First, we bring in the data file and create the route for getting the data.
// importing express
const express = require('express')
// getting the data file
const color = require('./data')
// creating a instance of express
const app = express();
// serving data
app.get('/api/colors', (req, res) => {
res.send(color)
})
app.listen(5000, console.log('App Running On Port 5000!'))
Run the server and go to localhost:5000/api/colors on your browser.

Wasn't that simple!

