Git and GitHub SSH Configuration
Configure SSH to your GitHub using git for better experiences with GitHub and GitHub
Installing git
Install git from here Choose a selection based on your operating system. For Linux and Ubuntu OS, you may use this alternative: Open your terminal and paste the command below:
sudo apt-get install git
Ensure you have a GitHub account. If not, create one here Join GitHub.
First of all, we’ll configure your details to git. “Assuming your GitHub username is DevAcc, and the email used on GitHub is devacc@mail.com” On your terminal, use the following commands:
$ git config --global user.name "devAcc"
$ git config --global user.email “devacc@mail.com”
To confirm the details, use git config --list With that set, you should be ready to start working efficiently with your local repository.

Generating a git ssh key
This prevents git from requesting your username and password every time you push into GitHub. (it’s annoying) So this is how we do it:
Open your terminal and use the commands below:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "devacc@mail.com"
This will prompt you to enter a location to save the key and create a password to access that.
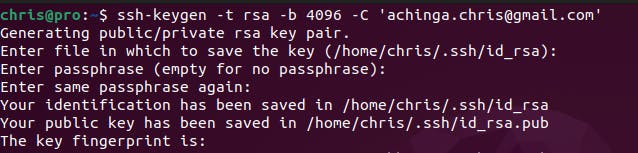
Connecting to Your GitHub Account
After this, you’ll need to copy the key to the clipboard. Use the command below to view the ssh key in a human-readable format:
cat < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
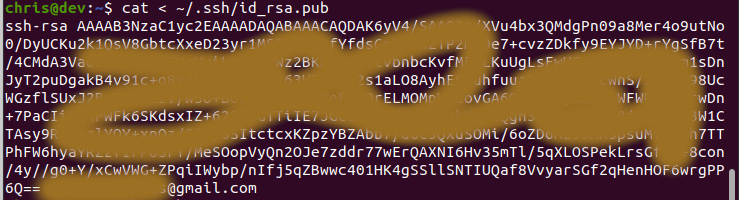
Note:
If you are using Windows PowerShell, use the command:
Get-Content "$env:USERPROFILE\.ssh\id_rsa.pub"
Copy the key displayed to your clipboard:
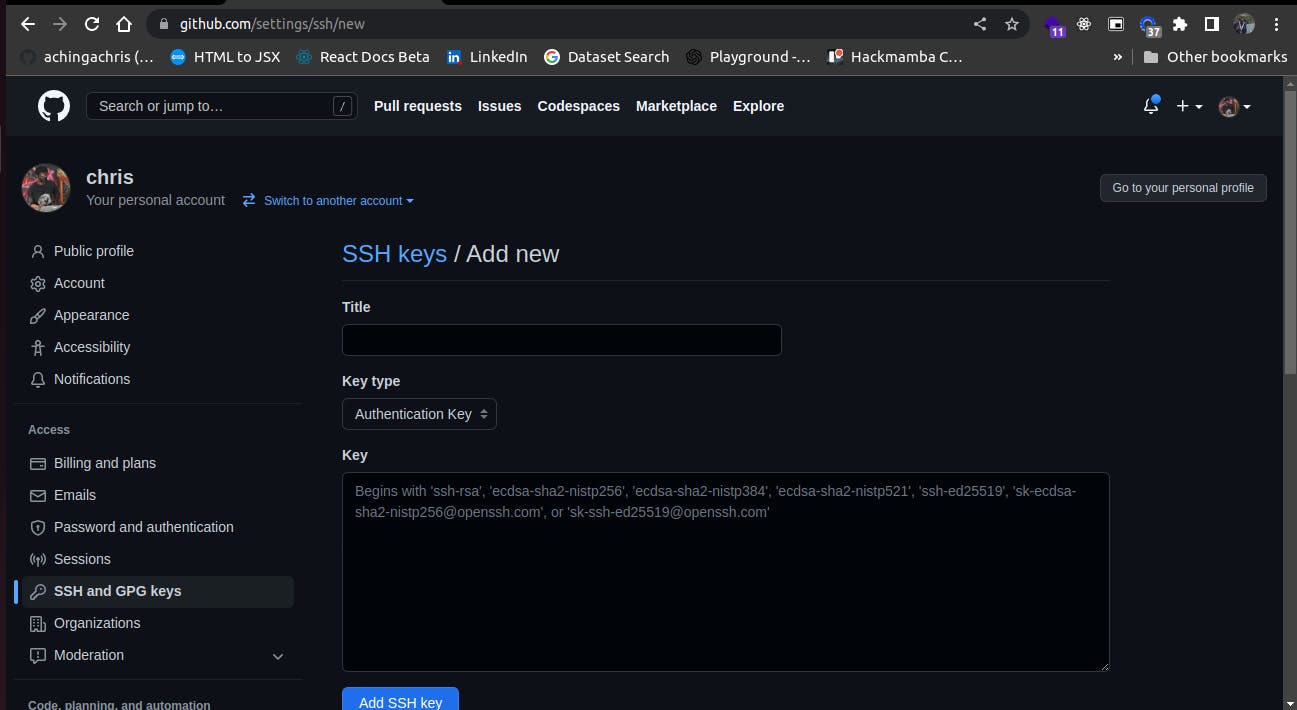
Go to your GitHub profile and navigate to settings, or better still use the link https://github.com/settings/ssh/new. On the left side, panel, click on SSH and GPG keys, then click on the top green button “New SSH” and paste the key there.
Voila! You are good to go

